
Creatine benefits and side effects: A Quick Guide to Muscle and Brain Health
Share
Creatine is a fantastic supplement for boosting muscle and brain health, but it's worth knowing about potential side effects, like a bit of temporary water retention. For most people, though, the advantages in strength, power, and cognitive function easily outweigh any minor, and usually avoidable, downsides.
What Is Creatine and How Does It Fuel Your Body?
Think of creatine as a rapid-recharge power bank for your muscle cells. It isn't some artificial substance; it's a natural compound your body already makes in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. You also get it from foods like red meat and fish.
When you get stuck into intense, short bursts of activity like lifting weights or sprinting, your cells burn through a high-energy molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This is your body's main fuel source. As you exert yourself, ATP breaks down to release energy, but your supply quickly runs low.
This is where creatine comes in. Its main job is to help regenerate ATP at lightning speed, essentially giving a spent energy molecule a fresh battery. By taking a supplement, you top up your body's creatine stores, making this rapid energy-recycling process even more efficient. This allows you to push harder for longer before fatigue kicks in.
This simple animation shows how your body uses creatine to generate ATP and power your muscles.
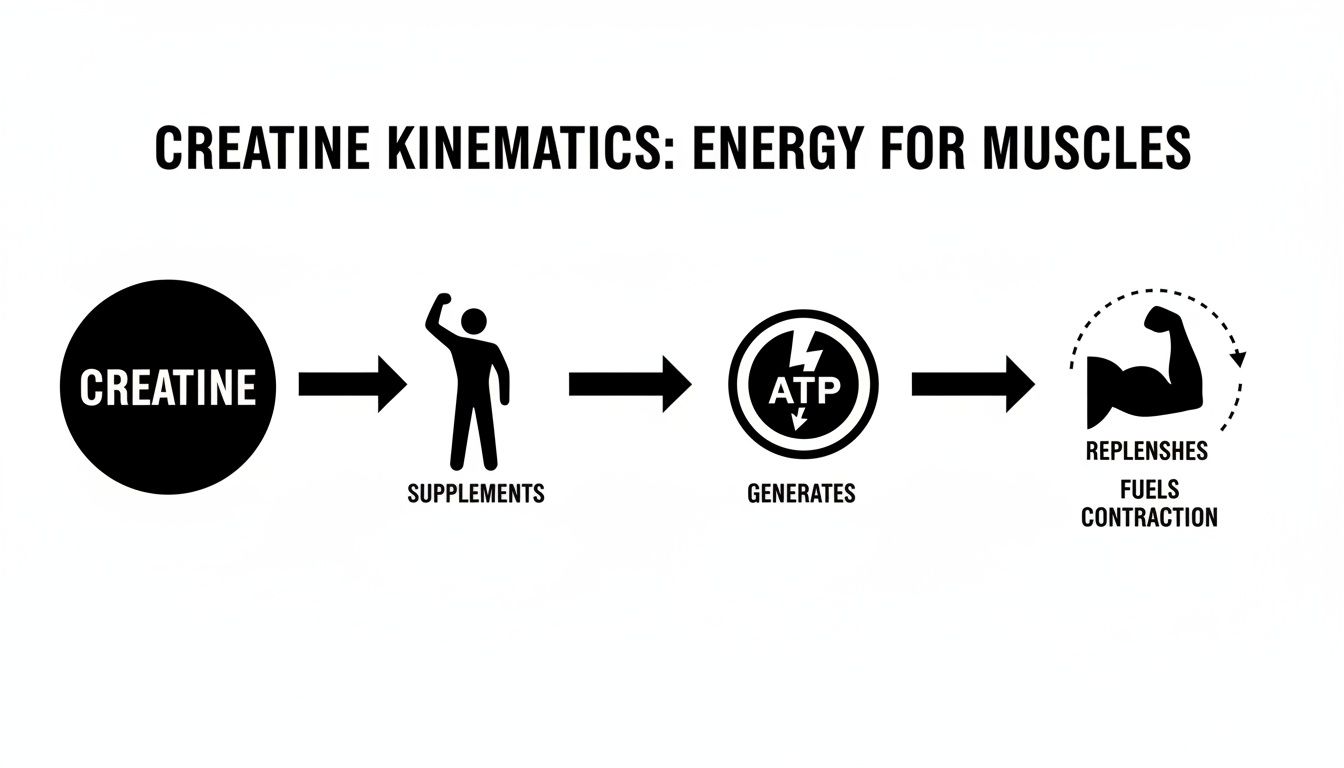
As you can see, creatine acts as a crucial middleman, turning used energy back into usable fuel for demanding physical tasks.
Why Is Creatine So Popular?
Creatine’s popularity isn't just based on gym lore; it's one of the most heavily researched sports supplements on the market. Its effectiveness is so well-documented that it’s become a staple for athletes and fitness enthusiasts across the UK.
You can see the growing awareness of its proven benefits in market trends. The UK creatine supplements market was valued at £31.1 million in 2023 and is projected to hit £80.2 million by 2030. This surge shows that more and more people recognise creatine's role in supporting strength and performance. You can read the full research about the UK creatine market to learn more.
Creatine supplementation is about more than just brute strength. By optimising cellular energy, it supports a chain reaction of benefits, from enhanced workout capacity to faster recovery and even sharper cognitive function.
Key Functions of Creatine
To put it simply, saturating your muscles with creatine leads to several direct boosts in performance. Here’s a breakdown of its core jobs:
- Rapid Energy Supply: It provides immediate fuel for high-intensity, short-duration exercises like weightlifting and sprinting.
- Increased Work Capacity: By regenerating ATP, it allows you to perform more reps or sets, leading to greater training volume over time.
- Cellular Hydration: Creatine pulls water into muscle cells, a process known as cell volumisation, which can support muscle growth.
Getting your head around this foundational mechanism is key to appreciating the wide range of benefits—and the odd side effect—we'll explore next. It all starts with fuelling your cells more efficiently.
The Science-Backed Benefits of Creatine

While creatine has a rock-solid reputation in the gym for building muscle, its advantages stretch far beyond the weight rack. Its main job—fuelling our cells with energy—unlocks a whole host of science-backed benefits for both body and mind.
By topping up those ATP energy reserves, creatine supplementation lets you push harder and with more intensity. And that’s the real catalyst for progress. Let’s break down the tangible gains you can actually expect.
Enhanced Strength and Power Output
First and foremost, creatine is brilliant for boosting strength and power. When you’re doing high-intensity stuff like lifting weights, your muscles need quick, explosive energy, and creatine makes sure it's right there on demand.
This translates into a very real improvement in your ability to lift heavier and produce more force. Study after study shows that people taking creatine see significant gains in their maximal strength, often within just a few weeks. You might find you can suddenly squeeze out an extra rep or two on your big lifts or add more weight to the bar sooner than expected.
And this boost isn't just for bodybuilders. It’s for anyone looking to improve their functional strength for sports or just everyday life.
Increased Lean Muscle Mass
Creatine helps you build muscle in a few clever ways. One of the key processes is something called cell volumisation, where it pulls water into your muscle cells. This doesn't just make your muscles look fuller; it also kicks off signals in the body that are involved in muscle growth.
On top of that, by letting you train harder and for longer, creatine increases the overall stimulus on your muscles. A greater workload is one of the main drivers of muscle hypertrophy (that's the technical term for growth).
This makes it a powerful ally for anyone wanting to build a leaner, stronger physique.
Improved Anaerobic Performance
Things like high-intensity interval training (HIIT), sprinting, and other all-out anaerobic activities need rapid energy production. This is where creatine truly shines, directly fuelling the explosive movements that define these kinds of workouts.
By ensuring your ATP stores are replenished almost instantly, it helps you maintain a higher intensity throughout your session. In practical terms, that means you can sprint faster, jump higher, and get your breath back more quickly between sets.
Research shows that creatine can improve performance in single and repetitive sprint activities by 1-5%. That might not sound like a lot, but in competitive sports or when you're chasing a personal best, it’s a massive edge.
Accelerated Recovery Between Workouts
One of the most overlooked benefits of creatine is its role in recovery. We all know that feeling after a tough workout—the microscopic damage to muscle cells that leads to inflammation and soreness. Creatine can help ease this in a couple of ways.
- Reduces Muscle Damage: It seems to help lower the markers of cell damage and inflammation that pop up after a strenuous session.
- Replenishes Glycogen: Some studies suggest it also helps you restock glycogen (your muscles' stored carbohydrate fuel) faster.
The upshot? You might feel less sore and be ready to hit the gym again sooner, which means more consistent and productive training over the long haul.
Emerging Cognitive and Brain Health Benefits
The benefits of creatine aren't just from the neck down. Your brain is an incredibly energy-hungry organ that also runs on ATP to do its job properly. New research is showing that creatine supplementation can support several cognitive functions.
Just as it helps your muscles during a tough workout, it can help your brain during mentally demanding tasks. This is especially noticeable when you're stressed or haven't had enough sleep.
- Fighting Mental Fatigue: Creatine can help reduce that feeling of mental burnout during challenging cognitive tasks.
- Supporting Short-Term Memory: Some studies point to potential improvements in working memory and how quickly you process information.
- Neuroprotective Properties: Researchers are even looking into its potential to help protect against certain neurological diseases.
The UK creatine market is starting to reflect these diverse uses, moving beyond just muscle building to embrace cognitive enhancement and recovery. With Europe holding over 30% of the global market share, UK consumers are increasingly seeking out high-quality products from trusted speciality retailers, backing up the growing awareness of creatine's wide-ranging benefits.
Understanding the Real Side Effects of Creatine

Creatine is one of the most heavily researched supplements on the planet, with a rock-solid safety profile. Yet, the myths just won't die. It's high time we separated the gym-floor gossip from the scientific facts.
When you take an honest look at the evidence, you quickly realise most of the so-called side effects are either minor, easily avoided, or based on complete misunderstandings. Our goal here is to give you a clear, no-nonsense picture so you can make a confident choice. The truth is, when used correctly, the vast majority of people only experience the upside.
Debunking the Water Weight Myth
The number one concern is "water weight," with many people worried it’ll make them look puffy or bloated. It’s a fair question, but it’s crucial to understand where this water actually goes.
Creatine works by pulling water into your muscle cells, a process known as intracellular hydration. Think of it like pumping up a tyre – it makes the muscle cells swell, giving you a fuller, firmer look. This isn't the same as the subcutaneous water retention that sits under the skin and causes that soft, bloated appearance.
In fact, this cellular hydration is a good thing. It contributes to a more muscular look and even plays a part in the cellular signalling that helps kick-start muscle growth and improve performance.
Managing Mild Stomach Discomfort
A small handful of people might run into minor gastrointestinal issues, like a bit of cramping or an upset stomach, especially when they first start. This is almost always down to taking too much at once or chugging it on an empty stomach.
Fortunately, this is incredibly easy to sidestep with a few simple tweaks:
- Take it with a meal: Having your creatine with food, especially some carbs, helps with absorption and acts as a buffer for your stomach.
- Stay hydrated: Creatine encourages your muscles to hold more fluid, so make sure you're drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Split your dose: If you're "loading" with a higher daily intake, just break it down into smaller 5-gram servings spread throughout the day.
For most people, these simple habits are all it takes to keep things comfortable.
The Myth of Kidney Damage in Healthy People
One of the most stubborn and damaging myths out there is the idea that creatine wrecks your kidneys. This rumour mostly comes from a misunderstanding of how we measure kidney function.
Taking creatine can slightly raise your levels of creatinine, which is a waste product that doctors look at in blood tests to check kidney health. But in this case, the rise in creatinine is simply a harmless byproduct of having more creatine in your system – it doesn't mean your kidneys are under strain.
Decades of research on healthy individuals have shown, time and time again, that using creatine at recommended doses does not harm kidney function. The scientific consensus on this is crystal clear.
Of course, if you have a pre-existing kidney condition, it’s vital to chat with your doctor before starting any new supplement. But for healthy folks, the evidence overwhelmingly points to it being safe.
Addressing the Hair Loss Rumour
The rumour linking creatine to hair loss all stems from a single, small study back in 2009. The study found that creatine increased levels of a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is linked to male pattern baldness.
Here's the catch: the study didn't actually measure hair loss, and the increase in DHT stayed within normal, healthy ranges. Since then, no other study has been able to replicate this finding. Major scientific reviews have looked at all the evidence and concluded that there's currently no strong proof to support the claim that creatine makes your hair fall out.
How to Take Creatine for the Best Results
Knowing what creatine does is one thing, but getting it to work for you is what really matters. To get the most out of this powerful supplement, you need a smart, consistent plan. Luckily, it’s much simpler than most people think.
This guide will walk you through the key choices you'll face—from picking the right type to nailing your daily dose—with clear, straightforward advice.
Choose the Right Form: Creatine Monohydrate
Step into any supplement shop and you'll be bombarded with different forms of creatine, from ethyl ester to hydrochloride (HCL). They all make big promises, but one form has consistently proven its worth in countless scientific studies: creatine monohydrate.
It’s the most researched, most effective, and usually the cheapest option you can find. There's no need to splash out on fancier, pricier versions. Simple, micronised creatine monohydrate powder is the gold standard for good reason.
The market reflects this. In the UK, creatine monohydrate is the top-selling form, with the market valued at £50.8 million in 2024 and expected to hit £80.47 million by 2033. Powder remains the go-to choice for its proven results and value for money, with some options costing as little as 24-33 pence per day.
Decide on a Dosing Strategy
So, how do you actually start taking it? There are two popular methods. Both get you to the same end point—muscles fully saturated with creatine—but one gets you there faster.
- The Loading Protocol: This is the fast-track approach. You take a higher dose of around 20 grams per day (often split into four 5-gram servings) for 5-7 days to quickly fill up your muscle stores.
- The Maintenance Protocol: This is the slow-and-steady route. You simply skip the high-dose phase and start with a daily maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day.
A loading phase will get you to peak saturation in about a week. The maintenance approach will take about three to four weeks. The choice is completely up to you and your personal preference.
Remember, the loading phase is completely optional. While it speeds things up initially, it offers no long-term advantage over a straight maintenance dose. If you have a sensitive stomach, sticking to the maintenance dose from day one is often the better choice.
To make the decision easier, here's a side-by-side look at the two strategies.
Choosing Your Creatine Dosing Strategy
This table compares the two most common creatine dosing strategies to help you decide which approach is best for your goals and lifestyle.
| Feature | Loading Protocol | Maintenance Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Saturate muscles as quickly as possible (in 5-7 days). | Saturate muscles gradually (in 3-4 weeks). |
| Daily Dose | 20 grams for 5-7 days, then 3-5 grams daily. | 3-5 grams daily from the start. |
| Best For | Individuals wanting the fastest possible performance benefits. | Anyone who prefers a simpler routine or has a sensitive stomach. |
| Potential Downsides | Higher chance of mild stomach discomfort or bloating initially. | It takes longer to experience the full benefits. |
Ultimately, both paths lead to the same destination. One is an express train, the other is a scenic route. Pick the one that fits your temperament and timeline.
Focus on Consistency Over Timing
One of the biggest myths around creatine is when to take it. Pre-workout? Post-workout? First thing in the morning?
The honest answer? It doesn't really matter all that much. The entire goal is to keep your muscle creatine stores topped up, and that’s achieved through consistent, daily intake.
Think of it like keeping your car’s petrol tank full. It doesn’t matter if you fill up in the morning or evening; what’s important is that you never let it run on empty. Taking your 3-5 gram dose every single day—including on rest days—is the key to seeing results.
If you want to fine-tune every last detail, some research suggests that taking it post-workout with carbs and protein might slightly boost absorption. This could be a tiny edge for those focusing on the best supplements for muscle recovery. For most people, though, the difference is negligible. Just find a time that works for you and make it a habit.
What Should You Mix It With?
Plain creatine monohydrate powder is mostly tasteless but can have a slightly gritty texture. To make it go down easier, just mix your daily dose into any liquid until it dissolves.
Here are a few simple ideas:
- Water: Can't go wrong with the basics. Just give it a good stir.
- Juice: The natural sugars in fruit juice can cause a small insulin spike, which may help your muscles absorb the creatine a little better.
- Your Protein Shake: This is probably the most popular and convenient method, especially if you already have a post-workout shake.
One thing to consider is caffeine. Some older studies hinted that caffeine might interfere with creatine's effects. While the evidence is a bit shaky, it might be wise to play it safe and separate your creatine dose from your morning coffee or pre-workout by an hour or so.
Is Creatine Right for Your Specific Goals?
Creatine isn't a one-size-fits-all supplement. Its effects really depend on who you are and what you're trying to achieve. The key is to look past the general advice and figure out how it can be tailored to your unique health and performance goals.
By understanding how creatine interacts with different body types and ambitions, you can personalise your approach to unlock its full potential. Think of it less as a blanket prescription and more as a specific tool in your health toolkit.
Creatine Benefits for Men
For men focused on fitness, creatine is a powerhouse for boosting strength, power, and muscle mass. Its main trick is rapidly refuelling ATP, the energy currency of your cells. This lets you push harder and go for longer during those intense training sessions.
This translates to greater training volume—more reps, more sets, and heavier weights—which is the fundamental driver of muscle growth. For men aiming to build a stronger, more athletic physique, a consistent daily dose of 3-5 grams can make a real difference over time. It quite literally supports the foundation of progressive overload.
Creatine Benefits for Women
There's a persistent myth that creatine will make women look "bulky." Let's clear that up: it won't. Due to hormonal differences, women don't build muscle in the same way men do, and creatine on its own isn’t going to change that.
What women can expect are benefits like improved strength, increased lean muscle tone, and better workout performance. Creatine simply helps you train with more intensity, which is exactly what you need to develop a lean, toned physique. On top of that, emerging evidence suggests it can support mood and cognitive function, making it a fantastic all-rounder for wellness.
For women, creatine should be seen as an energy and performance enhancer, not a bulking agent. It supports your training efforts to help you build strength and lean muscle without unwanted size.
Supporting Healthy Ageing in Older Adults
As we get older, we naturally start to lose muscle mass and strength. This condition, known as sarcopenia, can seriously impact mobility, balance, and overall quality of life. Creatine can be a valuable ally in pushing back against this age-related decline.
When paired with regular resistance training, creatine has been shown to help older adults build and maintain muscle more effectively than with exercise alone. It provides that extra bit of energy needed to perform strength exercises, which are absolutely vital for preserving functional independence.
- Improved Muscle Function: Helps maintain the strength needed for daily activities, like carrying the shopping or climbing stairs.
- Enhanced Bone Health: Strength training, which is powered up by creatine, can also help improve bone density.
- Better Cognitive Support: Just as it helps with physical energy, it can support brain energy, which is crucial for cognitive health as we age. For those interested, you can dive deeper into how certain compounds help with cognitive wellness in our guide to the best brain health supplements.
A Major Boost for Vegetarians and Vegans
Creatine is naturally found in animal products like red meat and fish. Because of this, people following vegetarian or vegan diets typically have lower baseline levels of creatine stored in their muscles.
This means that when they start supplementing, the effects can be even more dramatic. Vegetarians and vegans often experience more significant improvements in strength, performance, and even cognitive function compared to their meat-eating counterparts. For them, supplementing isn't just about optimisation; it's about replenishing stores that are naturally low due to their diet, making it a particularly powerful addition to their regimen.
Common Questions About Creatine Answered
Even after getting to grips with the science, a few practical questions always seem to pop up when people think about adding creatine to their routine. Let's tackle some of the most common ones with quick, clear answers, so you can feel completely confident about how it works.
Getting these final details straight is the last step in turning all that knowledge about benefits and side effects into a simple, practical plan you can actually follow.
Will Creatine Make Me Look Puffy or Bloated?
This is probably the number one question we hear, and it comes from a simple misunderstanding of "water weight." Creatine does increase the amount of water your body holds, but it pulls that water inside your muscle cells (intracellularly), not under your skin (subcutaneously).
Think of it as super-hydrating your muscles from the inside out. This process, known as cell volumisation, is actually a good thing. It contributes to a fuller, firmer muscle appearance and can even kickstart pathways that support muscle growth. It’s not the soft, puffy look that people associate with bloating.
So, while the number on the scales might tick up slightly when you first start, that's just your muscles filling out. The visual effect is a more athletic look, not unwanted puffiness.
Do I Need to Stop Taking Creatine Periodically?
The whole idea of "cycling" creatine—taking it for a few weeks, then stopping for a while—is a leftover habit from older, less-understood supplements. For creatine, it's completely unnecessary. It has one of the most solid safety profiles of any sports supplement out there, backed by numerous long-term studies confirming it's safe for continuous use in healthy people.
Continuous daily use is the most effective way to keep your muscle creatine stores fully saturated. Cycling off it simply lets these levels drop, which means you'll lose the performance benefits until you start the loading process all over again.
There’s no scientific evidence to suggest that cycling offers any extra benefits or reduces side effects. Sticking to a consistent daily maintenance dose of 3-5 grams is the best and most effective approach.
Should I Take Creatine on My Rest Days?
Yes, absolutely. The goal with creatine isn't about getting an immediate, pre-workout buzz; it's about keeping your muscle tissue saturated over the long term. Consistency is everything.
Taking it every day, including on the days you don't train, ensures your muscle creatine levels stay topped up and ready to go. That way, the energy reserves are always there for you when you next hit the gym. Skipping doses on your rest days will just slowly deplete your stores, making the supplement less effective. For a deeper dive into maintaining energy levels, check out our guide on the best supplements for fatigue.
Think of it like watering a plant. You do it consistently to keep the soil moist, not just on the sunny days. Taking creatine daily keeps your muscles primed for peak performance, day in and day out.
Ready to see how a personalised approach can optimise your health and performance? The Vitzai.com AI-driven questionnaire can help you identify your unique needs and build a smarter supplement stack. Take the free quiz today to get your tailored recommendations.
This article is for informational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult a qualified health professional before starting any new supplement or major lifestyle change.
