
Krill Oil v Fish Oil: Which Is Best for Omega-3?
Share
The whole krill oil v fish oil debate really boils down to two things: molecular structure and nutrient profile. Think of it like this: krill oil hands you omega-3s in a phospholipid form, which your body might absorb more readily. Fish oil, on the other hand, gives you a much higher dose of EPA and DHA, but in a triglyceride form.
So, the choice isn't just about which is 'better'—it's about whether you're after superior bioavailability or sheer omega-3 power.
Unpacking the Key Differences
Standing in the supplement aisle, it's easy to feel a bit lost between krill oil and fish oil. They’re both fantastic sources of the essential omega-3 fatty acids we all need—eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)—which are absolute powerhouses for your heart, brain, and joints. But where they come from and how they're built creates some important distinctions depending on your health goals.
Fish oil is the old guard, sourced from oily fish like salmon, sardines, and anchovies. It's been a staple in wellness for decades and has an enormous body of evidence behind it—we're talking over 30,000 studies that vouch for its benefits.
Krill oil is the newer kid on the block. It’s derived from tiny, shrimp-like crustaceans swimming in the pure, icy waters of the Antarctic Ocean. While the research library isn't as vast just yet, its unique properties are definitely turning heads in the nutrition world.
At-a-Glance Krill Oil vs Fish Oil
To make things a little clearer, here’s a quick side-by-side comparison.
| Feature | Krill Oil | Fish Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Form | Phospholipids – a structure your cell membranes love, making them easy to absorb. | Triglycerides – the standard form of fat found in most of the foods we eat. |
| Key Nutrients | EPA, DHA, Astaxanthin (a potent antioxidant), and Phospholipids. | Primarily high concentrations of EPA & DHA. |
| Bioavailability | Potentially higher; you may get away with a smaller, more efficient dose. | Very effective, but you might need a higher dose to achieve the same benefit. |
| Source | Antarctic krill (small crustaceans). | Oily fish (salmon, anchovies, mackerel). |
| Antioxidants | Naturally contains Astaxanthin, which gives it its red colour and protective properties. | Doesn't naturally contain astaxanthin. |
This table neatly sums it up: fish oil packs a bigger omega-3 punch in terms of raw numbers, but krill oil delivers its payload in a form that might be more readily used by your body, with an added antioxidant bonus.
The main point of divergence is how each oil actually delivers its omega-3s. This structural difference impacts everything, from how your body puts the nutrients to work to the dosage you might need to see results. Plus, krill oil has that powerful antioxidant, astaxanthin, which you won't find in most fish oil supplements.
To help you visualise it, here's a simple infographic.
As you can see, while fish oil might win on total omega-3 content, krill oil brings bioavailability and the antioxidant astaxanthin to the table.
It's easy to get caught up asking, "which one has more omega-3s?" But the real question should be, "which form of omega-3 can my body use most effectively?" Shifting your perspective this way is the key to choosing the right supplement for you.
Getting to grips with these foundational differences is the first step. Once you understand them, you're in a much better position to decide which oil aligns best with your body's needs and your personal health goals.
The Science: Phospholipids, Triglycerides, and Astaxanthin
When you get right down to it, the real showdown between krill oil and fish oil happens at the molecular level. It’s not just about where they come from; it’s about the very architecture of the omega-3s each one delivers. This fundamental chemistry is the key to how your body absorbs and uses these vital fats, influencing everything from the dose you need to how effective it is.
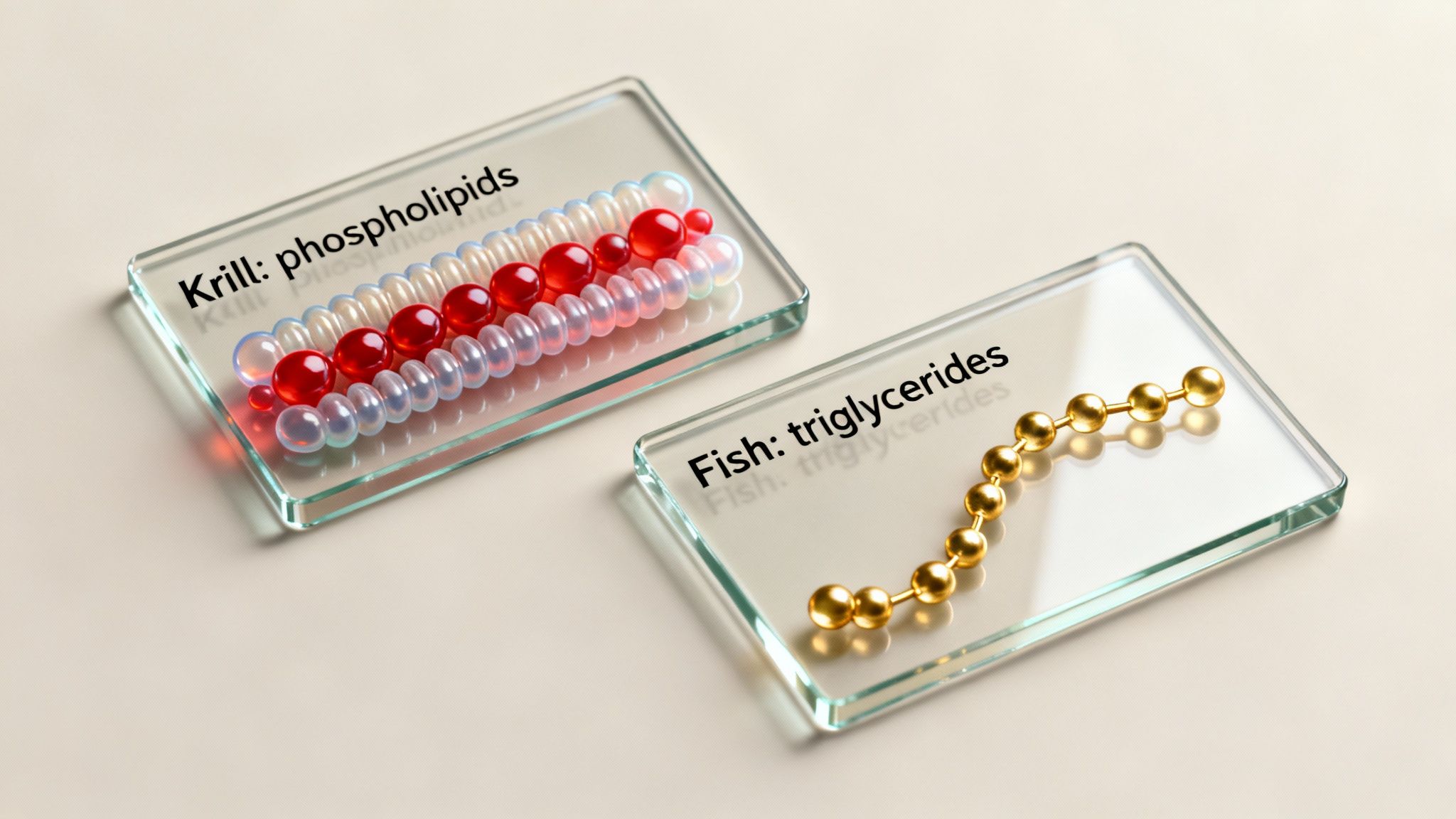
Fish oil serves up its omega-3 heavyweights, EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), in a triglyceride form. Picture a triglyceride as a simple storage unit: a glycerol ‘backbone’ with three fatty acids attached. This is the most common form of fat in our diet and in our bodies, so it’s a structure your digestive system already knows how to handle.
Krill oil, on the other hand, packages its EPA and DHA completely differently. Instead of being attached to triglycerides, they’re bound to phospholipids. This is a huge deal because the membranes of your own cells are also built from phospholipids. This like-for-like structure means the omega-3s from krill oil can slip into your cells much more easily.
Phospholipids vs Triglycerides
This distinction between phospholipids and triglycerides isn't just a bit of scientific trivia—it has real-world consequences for your health. Because phospholipids are water-soluble, they actually mix with the fluids in your stomach instead of sitting on top like other fats.
This simple property delivers a couple of key advantages:
- Better Absorption: The phospholipid structure helps omega-3s get absorbed more efficiently into your bloodstream and shuttled off to your cells.
- Fewer Side Effects: By blending with your stomach contents, krill oil is far less likely to cause those infamous "fishy burps" that can sometimes come with fish oil supplements.
The core difference is really in the delivery system. Fish oil uses a standard triglyceride vehicle—it works, but the body has to do a bit more processing. Krill oil uses a phospholipid vehicle, which is like a VIP pass, giving its omega-3s a more direct route into your cells.
This molecular head start means a smaller dose of krill oil can often provide similar benefits to a larger dose of fish oil. We'll dig into this more when we talk about bioavailability.
The Astaxanthin Factor in Krill Oil
Beyond its unique phospholipid setup, krill oil has another powerful molecule that fish oil doesn't: astaxanthin. This is a potent antioxidant from the carotenoid family, the same type of pigment that gives salmon its pinkish hue and carrots their bright orange. Krill get astaxanthin from the algae they eat, and it’s what gives krill oil its signature deep red colour.
But astaxanthin isn't just for looks. It plays two critical roles that add serious value to krill oil.
First, astaxanthin is a natural protector. It shields the delicate omega-3 fatty acids in krill oil from oxidation. Omega-3s are notoriously unstable and can go rancid easily when they’re exposed to light or air. Astaxanthin acts as a built-in preservative, keeping the EPA and DHA fresh and effective all the way from the capsule to your cells.
Second, astaxanthin brings its own impressive health benefits to the table. It’s known for fighting oxidative stress throughout the body, which is tied to inflammation, ageing, and chronic disease. Studies suggest astaxanthin can lend support to:
- Skin Health: By helping protect against UV damage.
- Eye Health: By supporting visual acuity and function.
- Joint Comfort: By helping to manage inflammation.
Fish oil supplements just don't have astaxanthin unless it's added in separately. Its natural presence gives krill oil an extra edge, offering both stability for the oil and added health perks for you. Grasping these molecular details—phospholipids for absorption and astaxanthin for protection—is key to making a smart choice between these two fantastic omega-3 sources.
How Your Body Absorbs Omega-3s from Each Source
When it comes to krill oil vs fish oil, one of the biggest differentiators is bioavailability. It’s a term that gets thrown around a lot, but what it really means is how much of the good stuff your body can actually absorb and put to work. It’s not just about the numbers on the label; it’s about how much EPA and DHA genuinely reaches your cells. This is where their different molecular structures really come into play.
Fish oil delivers its omega-3s in a triglyceride form. This is a common type of fat your body knows how to handle, but it needs a bit of help from digestive enzymes and bile salts to break it down before the fatty acids can be absorbed. Think of it as a package that needs to be carefully unwrapped by your digestive system first.
Krill oil, on the other hand, comes with its omega-3s already bound to phospholipids. This is a massive advantage because our own cell membranes are built from phospholipids. This structural head start means the omega-3s from krill oil can be absorbed and integrated into our cells far more easily, without all the extra digestive legwork.

The Phospholipid Advantage in Action
The phospholipid structure is what gives krill oil its edge in absorption. Because phospholipids are water-soluble, they mix right into the contents of your stomach. Fish oil, being a triglyceride, is a fat—it separates and floats on top of your stomach fluids, which is exactly why so many people complain about those infamous "fishy burps."
By blending seamlessly with stomach fluids, krill oil not only boosts absorption but also dramatically cuts down the chances of digestive upset. It just makes it a much friendlier option, particularly if you've got a sensitive stomach.
This superior absorption has a very practical takeaway: you can often get the same health benefits with a smaller dose of krill oil compared to a larger dose of fish oil. Studies have shown that the EPA and DHA from krill oil are more efficiently woven into our red blood cell membranes, a key marker of your body’s omega-3 status. If you want to dig deeper into the mechanics, exploring the science behind supplement absorption offers some great insights.
Market Trends and Consumer Awareness
People are catching on. The growing awareness of krill oil’s superior bioavailability is a huge reason for its surge in popularity. Take the UK market, for example, which was valued at around USD 875 million and is expected to hit USD 2.58 billion by 2035. This isn't just a fad; it reflects a smart shift from consumers who are looking for supplements that deliver efficiency, not just high potency. People are starting to look past the milligrams on the label and think more about how their body actually uses the nutrients.
This focus on absorption is changing the game. While marine oils are fantastic, it's good to know there are plant-based alternatives out there, too. You can learn more about them in our guide to vegan omega-3 supplements.
Ultimately, when you’re weighing up krill oil vs fish oil, the absorption factor is a powerful point in krill oil’s favour. If you’re looking for the biggest impact from a smaller, more comfortable dose, its phospholipid form is a compelling reason to make the switch. It all comes down to efficiency, better value, and a more pleasant experience—which is why bioavailability is at the heart of this debate.
Heart, Brain, and Joints: Where Does Each Oil Shine?
When you’re weighing up krill oil against fish oil, your specific health goals are what really matter. Both are fantastic sources of omega-3s, but they don't always deliver the same results for cardiovascular wellness, cognitive function, or joint health. Fish oil has a mountain of research backing it up, but krill oil’s unique structure gives it some compelling advantages in certain situations.
The market for these supplements is booming, especially in the UK. Fish oil products are set to grow at a CAGR of 7.6% in the coming years, which is well ahead of the global average. This isn't just a fleeting trend; it’s driven by a growing elderly population and a sharp increase in awareness about how omega-3s can help prevent chronic conditions affecting the heart, brain, and joints. This steady growth shows just how central it has become to wellness strategies across the UK.
With that in mind, it's crucial to understand which oil is the right fit for your body's needs.
Supporting Cardiovascular Health
For heart health, the conversation really revolves around managing cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood pressure. This is where fish oil has traditionally dominated, with an enormous library of over 30,000 studies showing its power to lower triglyceride levels – a major risk factor for heart disease. Time and again, higher doses of EPA and DHA from fish oil are linked to significant cardiovascular benefits.
But krill oil is proving to be a serious contender. Some studies suggest that even at lower doses, its phospholipid-bound omega-3s might be more effective at reducing LDL ("bad") cholesterol while boosting HDL ("good") cholesterol compared to fish oil. Plus, the astaxanthin in krill oil acts as a potent antioxidant, helping to prevent the oxidation of cholesterol, a process that contributes to plaque build-up in the arteries.
While fish oil is the established champion for hammering down triglycerides, krill oil's potential impact on cholesterol balance makes it a strong choice, particularly if you're looking for comprehensive heart support from a smaller, more easily absorbed dose.
Enhancing Brain Function and Mood
Both EPA and DHA are vital for brain health, but DHA is the star player here. It’s a primary structural component of your brain and retinas, essential for maintaining cognitive function, memory, and mood regulation as you age. Fish oil supplements, which are often rich in DHA, have long been the go-to for cognitive support for this very reason.
However, krill oil’s phospholipid form may give it a distinct advantage. Your brain has a very high concentration of phospholipids, so delivering omega-3s in this same structure could make it easier for them to cross the blood-brain barrier. In theory, this means more efficient support for your brain cells, neurotransmitter function, and overall cognitive performance. If you're focusing on long-term cognitive wellness, exploring the best supplements for longevity can offer a wider view.
Managing Joint Pain and Inflammation
Inflammation is the usual suspect behind joint pain and stiffness, especially in conditions like arthritis. Both krill and fish oil are celebrated for their anti-inflammatory properties, though they approach the problem from slightly different angles. Fish oil’s high concentration of EPA is incredibly effective at reducing key inflammatory markers throughout the body.
Krill oil, on the other hand, brings a one-two punch. Its omega-3s tackle inflammation directly, while the powerful antioxidant astaxanthin provides an extra layer of defence against the oxidative stress that can damage joint tissues. Clinical trials on krill oil have shown some really promising results, with participants reporting reduced pain and stiffness from rheumatoid and osteoarthritis, sometimes in as little as 7 to 14 days.
After discussing how krill and fish oils can support health by reducing inflammation, it's also helpful to understand what dietary elements might contribute to it. For a holistic approach to managing inflammation that benefits your heart, brain, and joints, consider learning about foods that cause inflammation to avoid them.
Sustainability, Purity, and Sourcing Compared
When you’re weighing up krill oil against fish oil, the discussion has to go deeper than just bioavailability and health perks. Where your supplement comes from—how it's sourced, its sustainability, and its purity—is just as crucial for both your own health and the planet's. The way these oils are harvested and processed has a direct line to their quality and environmental impact.
Let's be honest, fish oil sourcing can be a bit of a mixed bag. Its sustainability is entirely dependent on the type of fish being used and the fishing practices involved. While many reputable brands use small, fast-reproducing fish like anchovies and sardines from well-managed fisheries, others can contribute to the overfishing of larger species, which throws delicate marine ecosystems out of balance.
Krill oil, on the other hand, comes from tiny, shrimp-like crustaceans found in the Antarctic. The harvesting of Antarctic krill is actually one of the most tightly regulated industries on the planet, overseen by the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR). This organisation sets incredibly strict, precautionary catch limits to make sure the krill population stays stable, protecting the whales, seals, and penguins that rely on them.

Purity and Contaminant Risks
Purity is another major battleground in the krill oil vs. fish oil debate. Larger, longer-living fish such as tuna and mackerel can accumulate environmental toxins like heavy metals (mercury, lead) and PCBs over their lifespan. Although good fish oil brands use molecular distillation to purify their products, the initial risk of contamination is simply higher.
This is where krill has a massive natural advantage. They sit right at the bottom of the marine food chain and are harvested from the pristine, unpolluted waters of the Antarctic.
Because krill feed on phytoplankton and have short lifespans, they don't have the time to accumulate the same level of environmental contaminants as larger fish. This makes krill oil an inherently purer source of omega-3s from the outset.
This inherent purity, combined with its unique benefits, is driving some serious market growth. In fact, the UK krill oil market is expanding at a compound annual rate of about 9.5%. This reflects a clear consumer shift towards supplements that are seen as both clean and effective.
Making an Informed Choice
When you're picking out your omega-3, it pays to look for certifications that guarantee sustainable and ethical sourcing.
- For Fish Oil: Keep an eye out for labels like "Friend of the Sea" or the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) blue tick. These tell you the product comes from a fishery that meets strict standards for environmental responsibility.
- For Krill Oil: The MSC certification is the gold standard here, too. It ensures the krill was harvested in line with CCAMLR’s stringent guidelines.
Choosing a pure and potent supplement is key for your overall wellness. If you’re also interested in optimising your cellular energy alongside your omega-3 intake, our guide comparing ubiquinone vs ubiquinol CoQ10 offers some great insights into another vital supplement.
Ultimately, whether you land on krill or fish oil, prioritising a product that is both pure and sustainably sourced means you’re making a responsible choice for your body and the environment.
How to Choose the Right Omega-3 for You
So, how do you make the final call in the krill oil vs fish oil debate? It really boils down to matching the right tool to your personal biology, health goals, and lifestyle. There’s no single "best" choice for everyone; it's about what’s best for you.
At its core, the decision comes down to a simple trade-off: do you need a higher concentration of omega-3s, or is more efficient absorption your priority? Fish oil delivers a powerful, concentrated dose of EPA and DHA, backed by an enormous body of research. Krill oil, on the other hand, offers a smaller dose in a highly absorbable phospholipid form, with the added antioxidant punch of astaxanthin.
When Krill Oil Is the Smarter Choice
Krill oil really shines for people who prioritise efficient absorption and are looking for benefits that go beyond just omega-3s. Its unique molecular structure makes it a standout choice for specific needs.
You might lean towards krill oil if you:
- Have a Sensitive Stomach: Because krill oil's phospholipids mix with the contents of your stomach, it dramatically reduces the chance of those infamous "fishy burps" or any digestive upset.
- Want Maximum Joint Support: The one-two punch of easily absorbed omega-3s and the powerful anti-inflammatory antioxidant astaxanthin can be a game-changer for tackling joint pain and stiffness.
- Are Focused on Bioavailability: If you'd rather take smaller capsules or simply want to ensure your body is making the most of every single milligram, krill oil’s superior absorption efficiency makes it a fantastic option.
- Seek Cognitive and Skin Benefits: Astaxanthin provides an extra layer of defence against oxidative stress, which is brilliant for supporting long-term brain health and helping protect your skin from environmental damage.
For anyone looking for an efficient, gentle, and multi-faceted supplement, krill oil is often the way to go. Its enhanced absorption means a lower dose can still deliver impressive results, making it ideal for targeted, everyday support.
When Fish Oil Is the Right Tool for the Job
Don’t count fish oil out. It remains an incredibly effective and well-researched powerhouse, especially when getting a high concentration of EPA and DHA is your main goal. In certain situations, its straightforward, high-potency formula is simply unbeatable.
Fish oil is likely the better fit if you:
- Need a High Therapeutic Dose: For specific health targets, like aggressively lowering high triglyceride levels, the high concentrations of EPA and DHA found in fish oil are what healthcare professionals typically recommend.
- Prioritise a Vast Research Base: With over 30,000 studies to its name, the benefits of fish oil are documented more extensively than almost any other supplement. This offers a huge degree of confidence if you value long-standing scientific evidence.
- Are on a Tighter Budget: Generally speaking, fish oil provides more grams of omega-3s for your money, making it a more cost-effective choice for long-term daily supplementation.
How to Read the Label
Whichever you land on, knowing how to read the label is crucial. Always look for the total amount of EPA and DHA per serving, not just the total oil content.
Also, check for third-party purity certifications (like IFOS for fish oil) and sustainability seals (like MSC) to ensure you're getting a high-quality, responsibly sourced product. A good maintenance dose for most people is around 500 mg of combined EPA and DHA daily, though this can vary depending on your individual health needs.
By matching your personal goals with the unique strengths of each supplement, you can confidently add the power of omega-3s to your routine.
Your Questions Answered: Krill Oil vs. Fish Oil
Even after diving into the science, you might still be weighing things up. Let’s tackle some of the most common questions that pop up when choosing between krill and fish oil, so you can feel confident you’re making the right call for your health.
Can You Take Krill Oil and Fish Oil Together?
Technically, yes, but it’s rarely necessary and probably not the best use of your money. Since both supplements are fantastic sources of EPA and DHA, taking them at the same time often just leads to consuming more omega-3s than your body can effectively use. The real goal is to pick the one that’s a better match for your individual needs.
If you were to combine them, you’d get the sheer potency of fish oil with the smart absorption and antioxidant bonus of krill oil. The catch is that you’d have to be incredibly careful about your total EPA and DHA intake to avoid overdoing it. It’s always best to have a chat with a healthcare professional before you start mixing and matching supplements.
Which Is Better for Reducing Inflammation?
This is a close one. Both are brilliant at tackling inflammation, but krill oil seems to have a special knack for joint support. Fish oil is a true powerhouse for calming inflammation system-wide, thanks to its high concentration of EPA.
But krill oil comes at it from two angles. It delivers its omega-3s in that easy-to-absorb phospholipid form and throws in a potent antioxidant called astaxanthin. This unique antioxidant helps neutralise oxidative stress, a key driver behind inflammation and that nagging joint ache. In fact, some studies have shown krill oil can calm inflammation markers and ease arthritis symptoms in just a week or two.
For general, body-wide inflammation, a high-dose fish oil is an excellent, proven choice. But if you’re looking for more targeted relief, especially for your joints, krill oil’s one-two punch of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant action is hard to beat.
What Is the Best Time to Take Omega-3 Supplements?
The golden rule for both krill and fish oil is to take them with a meal that contains a bit of fat. This simple trick helps your body absorb the omega-3s much more efficiently and also sidesteps potential side effects like indigestion or those infamous "fishy burps."
Whether you pop your supplement with breakfast, lunch, or dinner doesn't really matter. What truly counts is consistency. Find a time that fits your daily schedule and stick with it. That steady supply of EPA and DHA is what allows your body to reap the long-term rewards for your heart, brain, and joints.
Ready to integrate a high-quality omega-3 into your daily routine? Let VitzAI help you build a personalised supplement stack tailored to your unique health goals. Discover your perfect fit at https://vitzai.com.
This article is for informational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult a qualified health professional before starting any new supplement or major lifestyle change.
