
Omega 3-6-9 Capsules: The Ultimate UK Explainer
Share
Walk down the supplement aisle, and you’ll likely see bottles proudly advertising "Omega 3-6-9". These combination capsules are designed to deliver three distinct types of fatty acids in one easy dose.
The idea is to offer a balanced intake of fats your body needs but might not be getting from food alone. But here’s the thing: while they're marketed for all-around wellness, most of us in the UK already get more than enough omega-6 and omega-9. This often makes a targeted omega-3 supplement a much smarter choice for tackling inflammation and boosting your overall health.
Understanding the Omega Fatty Acid Team

It helps to think of the different omega fatty acids as players on a team. Each one has a specific job to do, and for your body to perform at its peak, the team needs to be in balance. When certain players dominate the field—which is common in modern diets—it can lead to problems like chronic inflammation.
The Key Players Explained
The growing popularity of these supplements isn't surprising. It reflects a major shift towards preventative health, with the UK market for omega supplements expanding by around 7–8% annually in recent years. People are looking for practical ways to manage their health, and fats are finally getting the positive attention they deserve.
Here’s a simple breakdown of each team member:
- Omega-3s: The Anti-Inflammatory Stars. These are your MVPs for fighting inflammation. Your body can't make them from scratch, so they're 'essential'—meaning you must get them from your diet. They are absolutely crucial for heart, brain, and joint health.
- Omega-6s: The Energetic Offence. Also essential, these fats are vital for providing energy and supporting growth. The problem is, the modern UK diet is often overloaded with omega-6s from vegetable oils and processed foods. Too many can be pro-inflammatory, like an overly aggressive offensive line that keeps causing penalties.
- Omega-9s: The Reliable Support. This player is 'non-essential' because your body can produce it on its own. Found in healthy foods like olive oil and avocados, it offers steady support for cardiovascular health.
The core issue isn’t that omega-6 or omega-9 are "bad"—they're not. The problem is that our modern diets have created a massive imbalance. Most of us have far too much omega-6 and nowhere near enough omega-3, which is precisely why a focused omega-3 supplement is often the most effective strategy.
Grasping this dynamic is the first step toward making a smart choice for your health. If you're keen to learn more about different health-supporting options, you can browse through the general supplements category.
Next, we'll dive a bit deeper into what each of these fatty acids actually does in the body.
A Practical Guide to Each Omega Fatty Acid
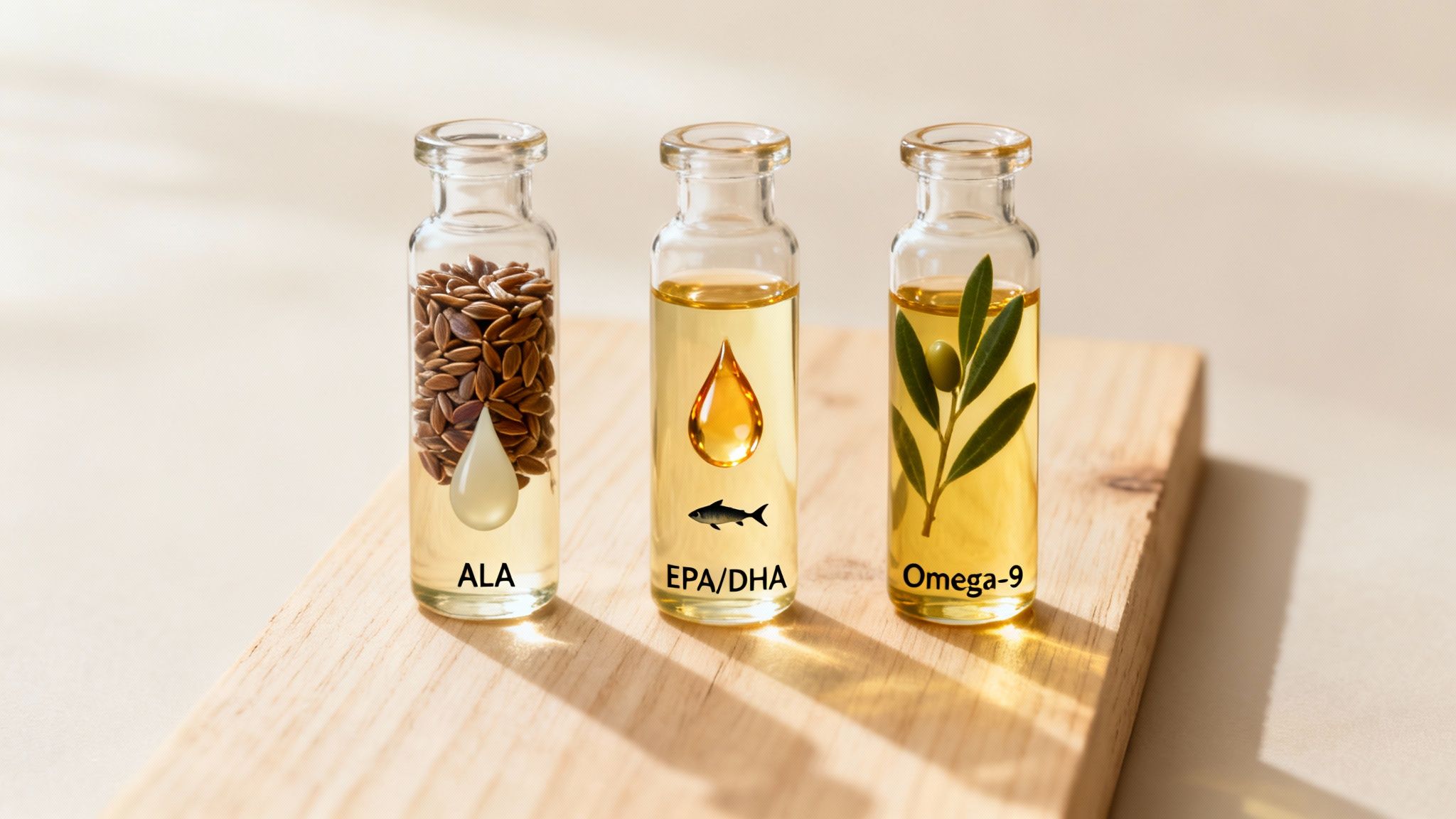

To really understand what omega 3-6-9 capsules are all about, it helps to break down what each of these fatty acids actually does inside your body. While they're often lumped together, each one has a very distinct role and comes from different places in our diet.
Getting to know them individually is the key. It's how you figure out which ones you genuinely need more of, and which you're probably getting plenty of already.
Understanding Omega-3: The Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouse
Let's start with the headliner: omega-3. These are essential polyunsaturated fats, a scientific way of saying your body can't make them from scratch. You absolutely have to get them from food. They’re famous for their powerful anti-inflammatory properties and are vital for pretty much every aspect of your health.
There are three main types you'll hear about:
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid): This is your plant-based omega-3, found in things like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Your body can technically convert ALA into the other two omega-3s, but the process is notoriously inefficient. For a deeper dive on this, check out our guide to vegan omega-3 sources.
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid): Found mostly in oily fish, EPA is a serious anti-inflammatory workhorse. It’s brilliant for supporting heart health and keeping joints comfortable by helping to dial down inflammation.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid): Also from oily fish, DHA is a major structural building block for your brain and the retina in your eye. It’s absolutely critical for sharp thinking, memory, and good vision.
Omega-6: The Essential but Often Overabundant Fat
Like omega-3s, omega-6 fatty acids are also essential polyunsaturated fats we need from our diet. They’re important for giving us energy, supporting healthy skin and hair, and maintaining bone health. Simple enough, right?
Well, here's where it gets complicated. The most common type of omega-6 in the modern Western diet—linoleic acid—can be converted into compounds that actually promote inflammation. The issue isn't that omega-6 is inherently bad; it's that most of us consume far too much of it. In the UK, it’s everywhere: in vegetable oils like sunflower and corn oil, processed snacks, and most takeaways. This creates a pro-inflammatory imbalance.
Omega-9: The Non-Essential Supporter
Finally, we have omega-9, which is a monounsaturated fat. The key difference here is that it’s non-essential—your body can actually produce this one itself. While you don't need to get it from your diet, it’s still incredibly good for you.
Think of omega-9 as a healthy bonus. It’s a hallmark of the Mediterranean diet, found in olive oil, avocados, and almonds. Eating it helps support your heart by improving cholesterol levels, but your body isn’t relying on you to top it up.
This is precisely why, for most people, supplementing with extra omega-6 and omega-9 is completely unnecessary. The real challenge for most of us is boosting our intake of the essential, anti-inflammatory omega-3s to get that crucial balance back.
Why the Omega-6 to Omega-3 Ratio Matters
Now that we know the individual players, let's talk about what is arguably the most important concept when you're looking at any omega supplement: the balance between omega-6 and omega-3.
Picture a seesaw in your body. On one side, you have the generally anti-inflammatory omega-3s, and on the other, the pro-inflammatory omega-6s. To keep everything running smoothly and inflammation under control, that seesaw needs to stay pretty level.
The Problem with the Modern British Diet
Go back a few generations, and our diets naturally provided a healthy balance. The ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 was somewhere between 1:1 and 4:1. The seesaw was perfectly balanced, which is exactly what our bodies are designed for.
Fast forward to today, and the typical Western diet—which is very common across the UK—has completely thrown a spanner in the works. With our reliance on processed foods, takeaways, and vegetable oils like sunflower and corn oil, most of us are now consuming a massive excess of omega-6. This has pushed the ratio to a frankly staggering 15:1 or even 20:1.
When that seesaw is tipped so heavily towards omega-6, it creates a constant, low-grade inflammatory state in the body. This kind of chronic inflammation is now understood to be a key driver behind many long-term health issues, from joint pain to cardiovascular problems.
This is the main reason why simply grabbing a combined omega 3-6-9 supplement might not be the smartest move for everyone. If your system is already overloaded with omega-6, adding even more of it just misses the point. The real goal for most people is to pile more omega-3s onto the other side of the seesaw to bring it back into balance.
Simple Swaps to Restore Your Balance
The good news is that you don't need to completely overhaul your life to start fixing this. A few simple, practical tweaks to your diet can begin to rebalance that internal seesaw. The goal isn't to get rid of omega-6 altogether—it's still an essential fat, after all—but to cut back on the excess while actively upping your omega-3 intake.
Here are a few real-world examples to get you started:
- Switch Your Cooking Oil: Ditch the sunflower or corn oil for cooking and opt for olive oil instead, which is rich in neutral omega-9. For things like salad dressings, consider flaxseed oil, a fantastic source of plant-based omega-3 (ALA).
- Prioritise Oily Fish: This is a game-changer. Try to get oily fish like salmon, mackerel, or sardines on your plate at least twice a week. They're the most direct and effective way to get the powerful anti-inflammatory omega-3s, EPA and DHA.
- Snack Smarter: Instead of reaching for crisps (often cooked in high omega-6 oils), swap them for a handful of walnuts or sprinkle some chia seeds over your yoghurt.
Making these small adjustments can have a huge impact on your omega ratio over time, helping to dial down underlying inflammation and support your health in the long run.
Choosing Between Omega 3-6-9 and Omega-3 Only
Trying to decide between a combined omega 3-6-9 capsule and a supplement focusing purely on omega-3 can feel a bit confusing. The truth is, the right choice really boils down to your diet. For most of us in the UK, the problem isn't a shortage of all fats, but a very specific lack of omega-3s.
This imbalance is exactly why a more targeted approach usually works better. By adding extra omega-6 and omega-9 that you likely don't need, a combined supplement might actually sidestep the real issue: a completely skewed fatty acid ratio.
When Might Omega 3-6-9 Capsules Make Sense?
While a focused omega-3 supplement is almost always the smarter strategy, there are a few niche situations where a 3-6-9 blend might be worth a thought. These are typically cases involving highly restrictive diets where getting a broad range of healthy fats is a genuine challenge.
You might consider a 3-6-9 blend if you are:
- On a very low-fat diet: If you're severely limiting all oils, nuts, and seeds, you could be falling short across the board.
- Recovering from a prolonged illness: Some conditions can mess with nutrient absorption, and a broad-spectrum fat supplement could offer some foundational support.
- Dealing with specific dietary limitations: If your diet is extremely limited and you rarely eat sources of omega-6 (like seeds) or omega-9 (like olive oil), a blend could fill in the gaps.
For the average person, though, this just isn't the case. Most UK diets are already swimming in omega-6 and have plenty of omega-9.
Why Omega-3 Only is Usually the Smarter Choice
The modern Western diet has pushed our internal balance of fats way out of kilter, heavily favouring the pro-inflammatory omega-6s over the anti-inflammatory omega-3s. It's not even a close contest.
Think of it like a seesaw. In a typical diet, the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 can be as high as 20:1, creating a constant, low-grade inflammatory state in the body.
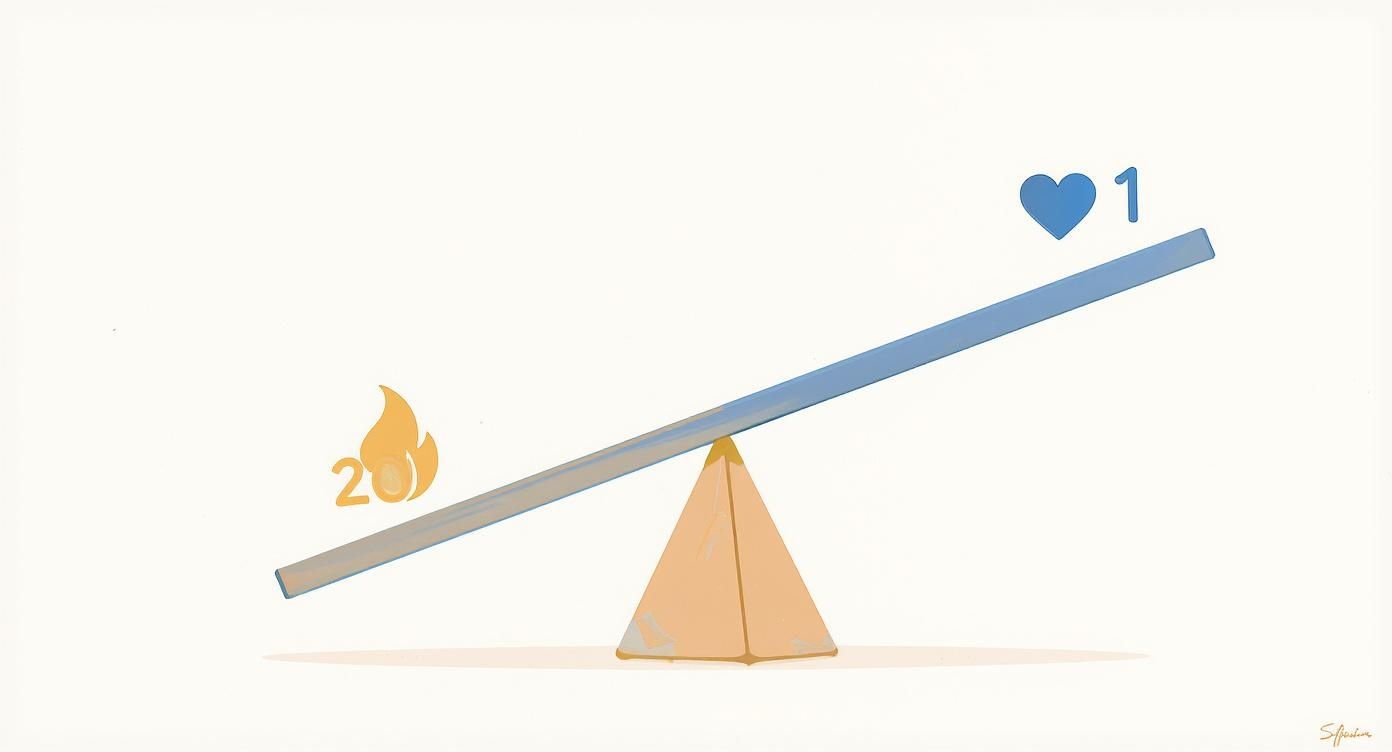
As you can see, the goal shouldn't be to add more weight to both sides of the seesaw. It’s about piling on the omega-3 to bring things back into balance.
Supplementing with a high-quality, omega-3-only product directly tackles this problem by boosting your intake of the most beneficial fatty acids, EPA and DHA. If you're curious about different omega-3 sources, our breakdown of omega-3 fish oil vs cod liver oil is a great place to start.
The most direct way to calm your internal inflammatory response is to up your intake of EPA and DHA. An omega-3 supplement is a precision tool for the job. A 3-6-9 blend is more of a scattergun approach that, for most people, is simply unnecessary.
Choosing the right supplement is about being strategic. If your diet is already giving you plenty of omega-6 and omega-9, putting your focus on a potent omega-3 supplement is what will deliver a real, noticeable impact on your health.
Omega 3-6-9 vs Omega-3 Only: Which Is Right for You?
So, how do you decide what's best for your personal situation? It comes down to honestly assessing your daily diet. This table breaks down the key differences to help you make an informed choice.
| Consideration | Omega 3-6-9 Capsules | Omega-3 (EPA/DHA) Only |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Individuals on extremely restrictive, low-fat diets who are deficient in all types of fatty acids. | The vast majority of people eating a typical Western diet, which is high in omega-6 and low in omega-3. |
| Primary Goal | To provide a broad spectrum of fats when dietary intake is severely limited across the board. | To correct the common omega-6 to omega-3 imbalance and reduce inflammation. |
| Dietary Context | Your diet lacks nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, olive oil, and oily fish. | Your diet includes vegetable oils, processed foods, and grains, but lacks sufficient oily fish. |
| Effectiveness | Can be counterproductive for most, as it adds more omega-6, potentially worsening the imbalance. | A targeted, effective strategy to increase beneficial EPA and DHA without adding unnecessary fats. |
Ultimately, the goal for most people should be to reduce their omega-6 intake from processed foods while actively increasing their omega-3 intake. An omega-3-only supplement is the most direct and efficient tool to help you do just that.
How to Select a High-Quality Omega Supplement

Walking down the supplement aisle can be overwhelming, but picking a genuinely good omega product is easier than it looks. When you’re ready to invest in your health, you want to know you're getting the real deal, not just a bottle of clever marketing.
The aim is simple: find a product that’s pure, potent, and easy for your body to actually use. This means the fatty acids inside can be absorbed effectively, delivering the benefits you're paying for. All it takes is a little know-how when reading the label.
Look for the True EPA and DHA Content
First things first, ignore the big number on the front of the bottle and flip it over. A capsule might boldly state "1000 mg Fish Oil", but the real story is in the nutritional information on the back. You need to find the specific breakdown of EPA and DHA.
These two compounds are the active ingredients doing all the heavy lifting, especially when it comes to fighting inflammation. Many cheaper supplements are bulked out with other fats, offering very little of the good stuff. A quality brand will clearly list the milligrams of both EPA and DHA, so you can be sure you're getting a meaningful dose.
If you're curious about how different sources of these oils stack up, our guide on krill oil versus fish oil is a great place to dig deeper.
Check the Molecular Form for Better Absorption
Omega-3s generally come in two forms: natural triglyceride (TG) and processed ethyl ester (EE). The best way to think about it is that the TG form is much closer to how you’d find fats in a whole fish. Because it’s more natural, your body recognises it and absorbs it far more easily.
The triglyceride form is widely considered to be more bioavailable than the ethyl ester form. In simple terms, this means more of the beneficial EPA and DHA actually gets into your system to do its job, making it a much more efficient choice.
While the EE form isn’t necessarily bad, it’s often a sign of a cheaper, more heavily processed product. If the label doesn't say which form it is, it's almost certainly the less absorbable EE form. Premium brands will always make a point of highlighting that their oil is in the superior triglyceride form.
Prioritise Purity and Sustainable Sourcing
Because fish can accumulate environmental toxins from the ocean, purity is something you can't compromise on. Look for proof of third-party testing from independent bodies like IFOS (International Fish Oil Standards). This certification is your guarantee that the product is free from harmful contaminants like heavy metals and PCBs.
Sustainable sourcing is just as important. Seals of approval from groups like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) or Friend of the Sea show that the fish were sourced with respect for our oceans.
Here in the UK, we're also seeing a huge shift towards plant-based options, with algae-derived omegas gaining serious traction. Some UK brands now report that their vegan products account for over 25–30% of their omega sales. This is fantastic news for consumers, offering excellent, sustainable choices whether you prefer wild-caught fish or vegan algae.
Common Questions About Omega Supplements
Even when you've got your head around the science, a few practical questions always pop up when you start a new supplement. When's the best time to take it? Can't I just get what I need from food? And what about side effects?
We've pulled together some of the most common queries we hear about omega supplements. This is your quick-fire guide to getting the most out of your capsules, safely and effectively.
What Is the Best Time of Day to Take Omega Capsules?
There isn't a single "best" time, but consistency is what really matters.
To get the most out of your supplement and dodge any digestive niggles (like those infamous fishy burps), always take your omega 3-6-9 capsules with a meal that contains some fat. The fat in your food is a helping hand, allowing your body to absorb the fatty acids in the supplement far more efficiently.
Lots of people find it easiest to take their capsules with breakfast or their evening meal to build a solid routine. The trick is to find a time that fits your day and stick with it, allowing those beneficial fats to build up in your system.
Can I Get All My Omegas from Diet Alone?
In theory, yes. But it takes a very specific and dedicated diet to pull it off. A menu packed with oily fish, nuts, and seeds will certainly give you a solid foundation of all three omega fatty acids.
The real challenge, however, is getting the higher, therapeutic doses of EPA and DHA—the key omega-3s—needed to genuinely support heart and brain health through food alone.
For most people in the UK, managing to eat oily fish like salmon or mackerel two or three times a week is a tough habit to maintain. That’s where a high-quality supplement becomes the most practical and reliable way to ensure you’re consistently getting enough of these crucial anti-inflammatory fats.
Are There Any Side Effects I Should Know About?
Most people get on with omega supplements just fine. When side effects do pop up, they’re usually mild and might include:
- A fishy aftertaste or "fish burps"
- Mild heartburn or indigestion
- Nausea or a slightly upset stomach
Taking your supplement with a meal is usually enough to prevent these issues. It's also really important to know that high doses of omega-3s can have a blood-thinning effect. If you're on any blood-thinning medication (like warfarin) or have surgery scheduled, you absolutely must speak to your doctor before starting an omega supplement.
How Long Until I Notice Any Benefits?
Patience is key here. Omega fatty acids aren't a quick fix; they work by gradually becoming part of your body's cell membranes. Think of it as a process of rebuilding from the inside out, which naturally takes time.
While some people might notice improvements in things like skin hydration or joint comfort within a few weeks, it typically takes two to three months of consistent daily use to feel more significant benefits. This could be changes in cognitive function, mood, or a reduction in overall inflammation. Sticking with it is what delivers the real, long-term results.
The Bottom Line
So, what's the final verdict on omega supplements? It's clear that these fatty acids are absolutely fundamental to keeping us healthy. But when it comes to choosing a supplement, it really boils down to your own diet and what you're hoping to achieve.
For most of us here in the UK, grabbing a dedicated omega-3 supplement is probably the smartest move. It’s the most direct way to tackle that all-too-common imbalance between our omega-6 and omega-3 intake, a direct result of the modern diet.
That said, an omega 3-6-9 blend isn't without its place. If your diet is particularly limited or has some very specific gaps, a combination capsule could be exactly what you need. Hopefully, with the information we’ve covered, you feel ready to pick out a top-quality product that genuinely fits your health journey.
This article is for informational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult a qualified health professional before starting any new supplement or major lifestyle change.
